Mislocated/Edge Weld
Definition
A weld that is incorrectly positioned compared to current workpiece design. Edge welds are those welds that touch or extend beyond the edge of the workpiece.
Description
Refer to company standards for acceptability of edge welds.
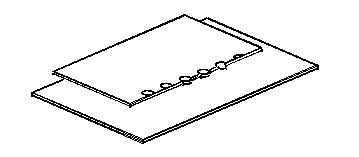
Fig. 1. Examples of edge welds
Detection
Preweld observation of tips on parts. Postweld visual inspection of parts to identify welds that are mislocated or extend beyond the edge of the workpiece.
Significance
Quality, Workplace Issues, Cost, Downtime, Maintenance, Throughput (cycle time; PPH) are all potentially affected by this condition. Special considerations are noted below:
- Quality: Subsequent fitting or and operation of rubber seals may be impaired by edgewelds. Mislocated welds may affect NVH, sealing etc.
Possible Causes
Strong Possibilities
- Electrode Face Not Parallel to Workpiece
- Inadequate Electrode Alignment
- Incorrect Workpiece Selected
- Poor or Varying Part Fit-up
- Poor Weld Accessibility
- Weld Flange Too Small
- Weld Wrongly Located
- Wrong Tips
Weak Possibilities
Nonmatrix Possibilities
- Edge welds can cause high levels of expulsion