Wrong Transformer
Definition
The weld is not correctly made due to the use of an improper transformer.
Description
Transformer size is defined by both the secondary voltage and the thermal rating (kVA).
- Transformer too small: Weld is not formed because the maximum secondary voltage is too low to drive the required weld current. The transformer fails because the weld schedule exceeds the thermal rating (kVA). The thermal loading of the transformer is dependant on the Duty Cycle of the machine. Squeeze time allows the welding tip force to stabilize before the current is applied (see figure). If the current is applied before the force is stabilized, several phenomena are possible: Surface expulsion could occur, resulting in premature electrode wear.
- Transformer too large: Weld is not made due to excessive secondary voltage on low tap.
Duty Cycle = (Timeon)/(Timeon + Timeoff) in a one minute period.
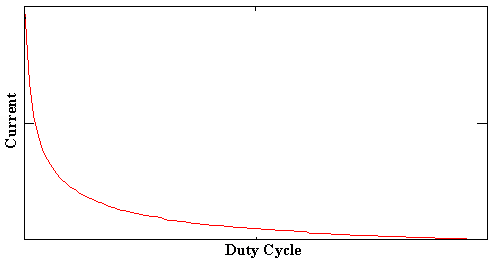
Weld Current vs. Duty Cycle for a Given Transformer
Detection
Detection evidence may include:
- Cracks and Holes
- Excessive Indentation
- Expulsion/Burn Through
- Inconsistent Weld Quality
- Missing Weld
- Nonround Weld
- Poor Class A Appearance
- Stuck Weld
- Undersized Weld
- Sticking/Stuck Tips
- Incorrect transformer color (for color coded transformers)
- Improper primary voltage (check nameplate)
- Improper frequency (check nameplate)
- Improper kVA rating (check nameplate)
Significance
Quality, Workplace Issues, Cost, Downtime, Maintenance, Throughput (cycle time; PPH), are all potentially affected by this condition. Special considerations are noted below:
Maintenance: Transformers with excessively high secondary voltage resulting in high secondary currents can cause other components in the secondary loop to fail.
Subordinate Causes
- Correct transformer not immediately available
- Inadequate operator training
- Improper identification
- Check secondary configuration (series, parallel or one side firing)